Peace of Mind for Your Family & Orderly Transition of Assets

“In this world nothing can be said to be certain, except death and taxes.”
– Benjamin Franklin
Nearly 230 years later … truer words were never spoken! There is no cure for either, but there are strategies to mitigate the effect of taxes in the event of death or disability.
That brings us to the topic of Estate Planning to deal with the unknown future as it relates to health and longevity of life, provide peace-of-mind for your family and create an orderly transition of assets in the event of death or disability. Additionally, as accountants, we seek to assist with all of the above in the most tax-favored ways possible.
A quick statistic: Approximately 55 percent of American adults do not have a will or other estate plan in place, according to LexisNexis.

The Perils in the Absence of Adequate Estate Planning
In the absence of adequate estate planning, disability due to illness or injury can multiply otherwise avoidable legal and financial challenges. For example, one mistaken belief by many married couples is that financial and health care decisions can be made for one another in the event either spouse becomes disabled. Not necessarily true!
The able-bodied spouse may not automatically have access to the disabled spouse’s medical information and finances.
Likewise, in the event of death, there should be a carefully developed roadmap for the distribution of the deceased’s assets, minimize estate and transfer taxes, specify care for minor children and minimize or eliminate preventable conflicts among family and heirs.
The solution to this is the subject of this article – a properly crafted Estate Plan to protect, preserve and manage your estate in the event of death or disability.
Note: Your last name does not have to be Gates, Bezos or Zuckerberg to be a candidate for an estate plan. Virtually anyone 18 years old, married or single, should arrange for a trusted representative to make personal, health care and financial decisions in the event of incapacity to do so or death.
Selection of Your Decision Makers
 A critical element of your plan is your selection of decision makers, i.e. the executors, trustees, agents and guardians who will shoulder significant responsibilities on your behalf. Choices should never be made simply because an individual is a family member or close friend. Your selection should reflect the individual’s capabilities and willingness to fulfill the required duties of the role he or she is expected to play.
A critical element of your plan is your selection of decision makers, i.e. the executors, trustees, agents and guardians who will shoulder significant responsibilities on your behalf. Choices should never be made simply because an individual is a family member or close friend. Your selection should reflect the individual’s capabilities and willingness to fulfill the required duties of the role he or she is expected to play.
Choosing the executor of your estate is perhaps the single most important decision you will make to deal with the unknown future, provide peace-of-mind for your family and create an orderly transition of assets in the event of death or disability.
Competency, harmony and willingness to serve are the key ingredients to a successful choice of an executor. Let’s take a look at each.
- Competency: Your choice of an executor is not that of a popularity contest, nor the age-ranking of a family member. Choices should never be made simply because an individual is a close friend , your oldest child or concern for hurting someone’s feelings. Your selection should reflect the individual’s capabilities, competencies and willingness to serve.
- Harmony: In some instances, it may be prudent to appoint two or more adults as joint executors. Be thoughtful! Choosing two or more executors who have no history of successfully working together may create a confrontational atmosphere leading to less than efficient management of your affairs.
- Willingness: Assuming the executor candidate is competent, it is important to determine that person’s readiness to assume the required duties of the role. Depending on the complexity of the estate, it may be a far more overwhelming task than expected. Additionally, there are potential legal liabilities for negligent handling of the estate.
- Third-Party Choices: If there are no clear choices of an individual or compatible multiple of individuals to fulfill the role of executor, you may appoint an entity such as a bank, trust company or a law firm that offers executor services.
Now consider all of the above in the context of complexity of the estate, possible warring beneficiaries and outstanding legal issues. It may be a simple undertaking with a modest estate. It may prove daunting in an estate with multi-faceted intricacies. Remember, this will be a one-time, part-time job for an individual executor and may require a broad range of skills.
Of course, expertise does not have to be personally demonstrated in all aspects of “a day in the life of an executor”, as there is plenty of help available from a capable team of accounting, legal and investment professionals.
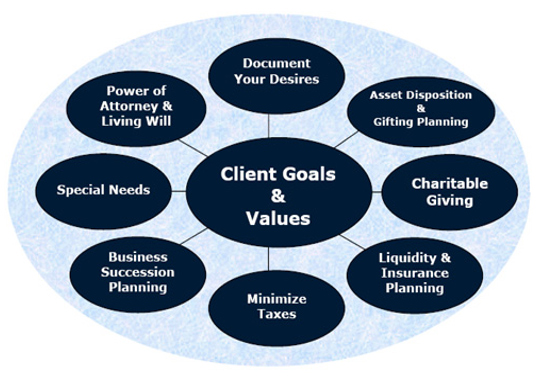
Creating Your Estate Plan
Estate Planning is not a do-it-yourself project. Your best course of action is to seek help from experienced experts who specialize in estate planning matters. Once chosen, your advisors will determine the issues to be addressed and the appropriate documentation required to ensure instructions consistent with your desires.
Among the documents your advisors may recommend are a Will; Durable Power of Attorney for Health Care Decisions; Living Will; Durable Power of Attorney for Financial Matters, one or more Trusts; and a HIPAA Authorization. Estate plans do not lend themselves to one-size-fits-all, so the specifics of yours will be determined based on your needs, desires and estate valuations.
Summary
If the above appears daunting to you, that just underscores the need for competent, experienced estate planning advice. As you may anticipate, with so many possible combinations of documents and provisions of each, there is the potential for even simple mistakes to wreak havoc on the validity of your Estate Plan.
Your attorney and accountant will likely collaborate to ensure tax and other financial issues are properly addressed. Additionally, your financial advisors and bankers will be invaluable in offering guidance on planning the proper asset allocation and investment management of your estate.
Of course, at Pearson & Co. our work as accountants is to maximize your estate value and minimize your tax bite. In serving you, we can also introduce you to skilled estate planning professionals. If we can help with a referral … just ask.




























 A critical element of your plan is your selection of decision makers, i.e. the executors, trustees, agents and guardians who will shoulder significant responsibilities on your behalf. Choices should never be made simply because an individual is a family member or close friend. Your selection should reflect the individual’s capabilities and willingness to fulfill the required duties of the role he or she is expected to play.
A critical element of your plan is your selection of decision makers, i.e. the executors, trustees, agents and guardians who will shoulder significant responsibilities on your behalf. Choices should never be made simply because an individual is a family member or close friend. Your selection should reflect the individual’s capabilities and willingness to fulfill the required duties of the role he or she is expected to play.